Experiments with photosynthesis:
how carbon dioxide is converted into oxygen
how carbon dioxide is converted into oxygen
1Preparations
Since the usual concentration of carbon dioxide in natural air is only about 0.03%, it is rather difficult to observe changes in CO2 or O2 concentration in a gas detector tube.
However, the change appears clearly, if you use the following procedure.
You will need
- One leafy potted plant
- One sturdy polyethylene bag (5 to 10 litre capacity)
- One drinking straw
- Adhesive tape (cellophane tape etc.)
- Scissors
- Gas detection equipment, comprising:
- Gas sampling pump
- Carbon dioxide detector tube 2EL
- Carbon dioxide detector tube 2EH
- Oxygen detector tube 31E
2Enclosing the plant in the plastic bag and filling it with exhaled air
- 2-1
- Attach two strips of adhesive tape to two opposite sides of the plastic bag as reinforcement. With the scissors make a small incision in each of the two reinforced places. Then cover each slit with another strip of tape and fold it for added strength so that air cannot leak.
- 2-2
- The stalk and leaves of the plant are enclosed in the plastic bag (leaving the roots and pot exposed) and wound tightly with adhesive tape at the base to seal it airtight.

- 2-3
- Peel off one of the upper strips of adhesive tape, and poke a straw through the slit. Then blow (5 - 10 times) into it after taking slow deep breaths. Immediately reseal the slit.

3The initial condition is examined and recorded
- 3-1
- Insert the carbon dioxide detector tube 2EH in one gas sampling pump, and oxygen detector tube 31E in another gas sampling pump. Peel off the upper strips of adhesive tape, and poke the tip of one detector tube through one slit and the other tube through the other incision. Then proceed to respectively measure the oxygen as well as the carbon dioxide concentrations and record the values.
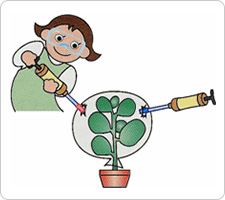
- 3-2
- Reseal the two incisions with strips of adhesive tape
4Changes in gas concentration (over time) are measured
- 4-1
- Leave the plant exposed to direct sunlight for several hours, and then respectively measure the oxygen as well as the carbon dioxide concentrations and record the values.
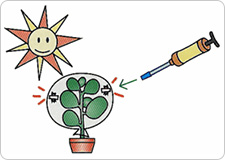
5Interpreting the experiment results
Sample experimental data
| Oxygen | Carbon dioxide | |
|---|---|---|
| Start | approx. 18% | approx. 3.6% |
| 1 hour later | approx. 18.5% | approx. 2.7% |
| 3 hour later | approx. 19.5% | approx. 1.5% |
When plants perform photosynthesis the amount of carbon dioxide
is reduced and the amount of oxygen increases!
-
Experiments with Detector Tubes
-
Let's think together

